publications
publications by categories in reversed chronological order.
2025
-
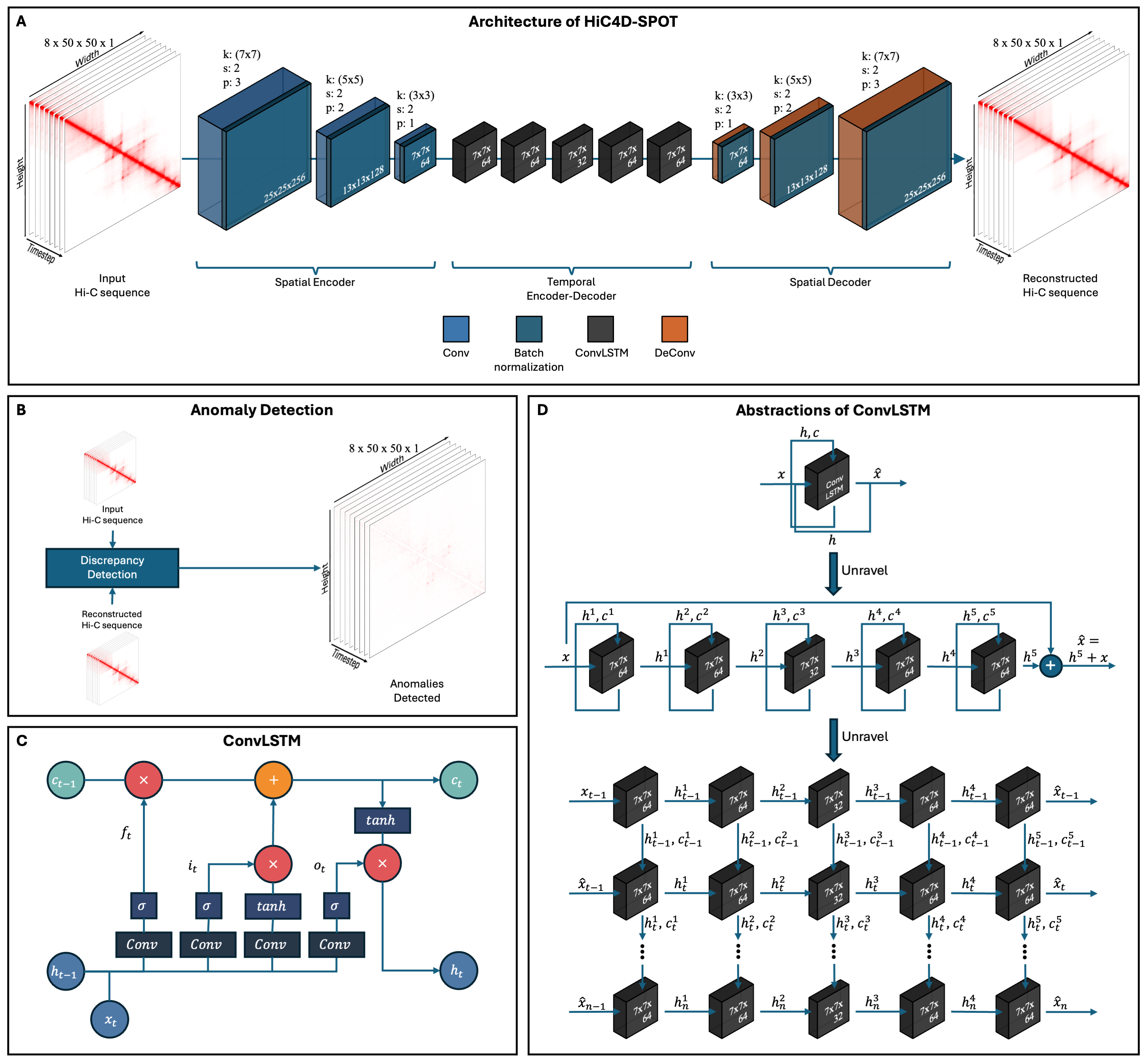 HiC4D-SPOT: a spatiotemporal outlier detection tool for Hi-C dataBishal Shrestha, and Zheng WangBriefings in bioinformatics, Jul 2025
HiC4D-SPOT: a spatiotemporal outlier detection tool for Hi-C dataBishal Shrestha, and Zheng WangBriefings in bioinformatics, Jul 2025The 3D organization of chromatin is essential for the functioning of cellular processes, including transcriptional regulation, genome integrity, chromatin accessibility, and higher order nuclear architecture. However, detecting anomalous chromatin interactions in spatiotemporal Hi-C data remains a significant challenge. We present HiC4D-SPOT, an unsupervised deep-learning framework that models chromatin dynamics using a ConvLSTM-based autoencoder to identify structural anomalies. Benchmarking results demonstrate high reconstruction fidelity, with Pearson Correlation Coefficient and Spearman Correlation Coefficient values of 0.9, while accurately detecting deviations linked to temporal inconsistencies, topologically associating domain (TAD) and loop perturbations, and significant chromatin remodeling events. HiC4D-SPOT successfully identifies swapped time points in a time-swap experiment, captures simulated TAD and loop disruptions with high confidence scores and statistical significance of 0.01, and detects HERV-H boundary weakening during cardiomyocyte differentiation, as well as cohesin-mediated loop loss and recovery—aligning with experimentally observed chromatin remodeling events. These findings establish HiC4D-SPOT as an efficient tool for analyzing 3D chromatin dynamics, enabling the detection of biologically significant structural anomalies in spatiotemporal Hi-C data.
-
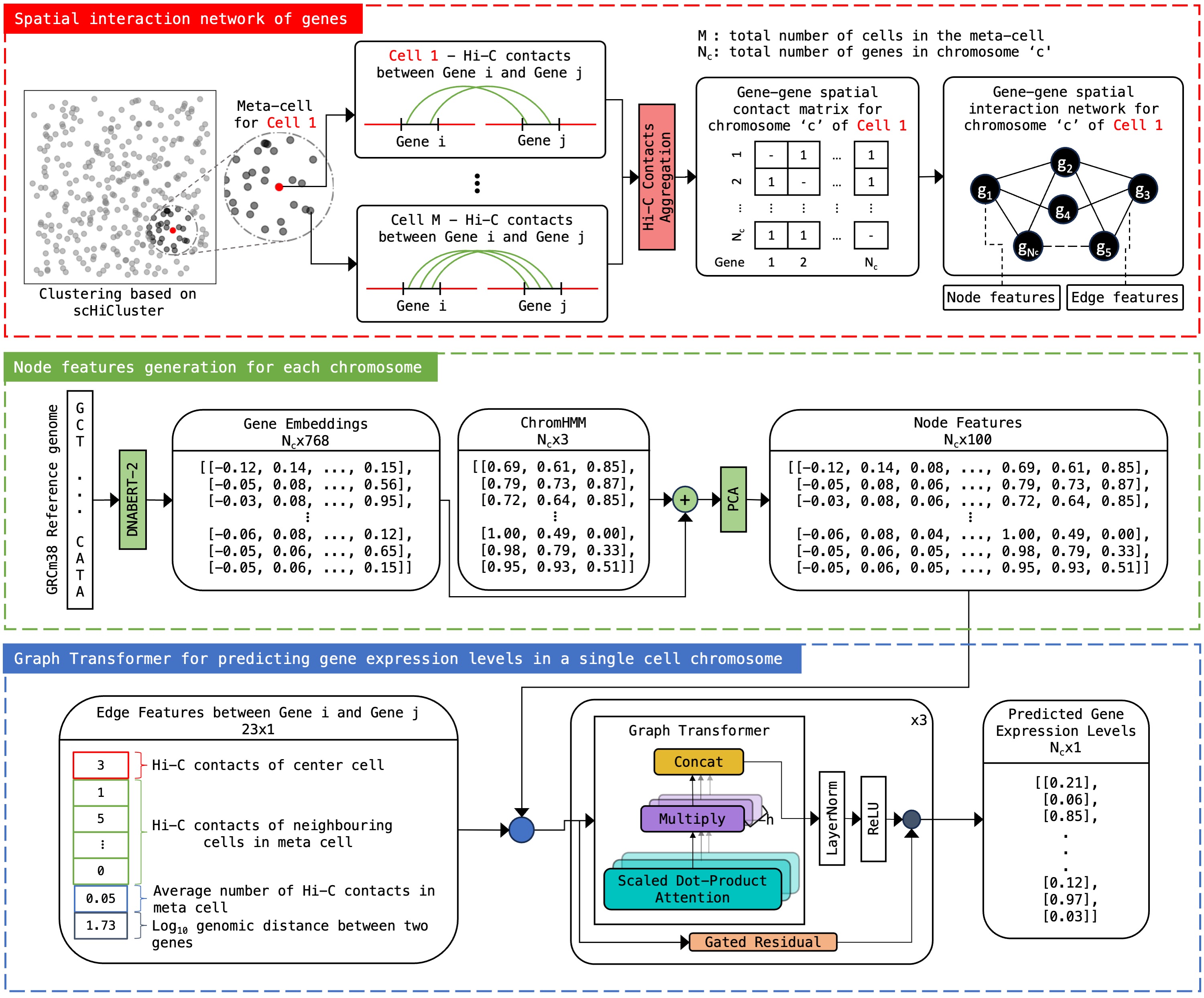 scHiGex: predicting single-cell gene expression based on single-cell Hi-C dataBishal Shrestha, Andrew Jordan Siciliano, Hao Zhu, and 2 more authorsNAR Genomics and Bioinformatics, Jan 2025
scHiGex: predicting single-cell gene expression based on single-cell Hi-C dataBishal Shrestha, Andrew Jordan Siciliano, Hao Zhu, and 2 more authorsNAR Genomics and Bioinformatics, Jan 2025A novel biochemistry experiment named HiRES has been developed to capture both the chromosomal conformations and gene expression levels of individual single cells simultaneously. Nevertheless, when compared to the extensive volume of single-cell Hi-C data generated from individual cells, the number of datasets produced from this experiment remains limited in the scientific community. Hence, there is a requirement for a computational tool that can forecast the levels of gene expression in individual cells using single-cell Hi-C data from the same cells. We trained a graph transformer called scHiGex that accurately and effectively predicts gene expression levels based on single-cell Hi-C data. We conducted a benchmark of scHiGex that demonstrated notable performance on the predictions with an average absolute error of 0.07. Furthermore, the predicted levels of gene expression led to precise categorizations (adjusted Rand index score 1) of cells into distinct cell types, demonstrating that our model effectively captured the heterogeneity between individual cell types. scHiGex is freely available at https://github.com/zwang-bioinformatics/scHiGex.
2023
- arXiv
 Adversarial sample generation and training using geometric masks for accurate and resilient license plate character recognitionBishal Shrestha, Griwan Khakurel, Kritika Simkhada, and 1 more authorJan 2023
Adversarial sample generation and training using geometric masks for accurate and resilient license plate character recognitionBishal Shrestha, Griwan Khakurel, Kritika Simkhada, and 1 more authorJan 2023Reading dirty license plates accurately in moving vehicles is challenging for automatic license plate recognition systems. Moreover, license plates are often intentionally tampered with a malicious intent to avoid police apprehension. Usually, such groups and individuals know how to fool the existing recognition systems by making minor unnoticeable plate changes. Designing and developing deep learning methods resilient to such real-world ’attack’ practices remains an active research problem. As a solution, this work develops a resilient method to recognize license plate characters. Extracting 1057 character images from 160 Nepalese vehicles, as the first step, we trained several standard deep convolutional neural networks to obtain 99.5% character classification accuracy. On adversarial images generated to simulate malicious tampering, however, our model’s accuracy dropped to 25%. Next, we enriched our dataset by generating and adding geometrically masked images, retrained our models, and investigated the models’ predictions. The proposed approach of training with generated adversarial images helped our adversarial attack-aware license plate character recognition (AA-LPCR) model achieves an accuracy of 99.7%. This near-perfect accuracy demonstrates that the proposed idea of random geometric masking is highly effective for improving the accuracy of license plate recognition models. Furthermore, by performing interpretability studies to understand why our models work, we identify and highlight attack-prone regions in the input character images. In sum, although Nepal’s embossed license plate detection systems are vulnerable to malicious attacks, our findings suggest that these systems can be upgraded to close to 100% resilience.